Recommendations for AI in Teaching

 Recommendations for AI in teaching
Recommendations for AI in teaching
A Human-Centered Approach
A human-centered approach to AI in teaching emphasizes the critical role of educators in guiding and interpreting AI-supported learning processes. Rather than allowing AI to make autonomous decisions, this approach ensures that instructors remain actively involved in identifying patterns in student behavior, assigning meaning to those patterns, and making key instructional choices. It supports teacher-led formative assessments and encourages reflective planning and intervention strategies, such as Response to Intervention. Since AI lacks the nuanced contextual judgment that humans possess, educators must retain control and responsibility for decisions that impact student learning, well-being, and equity. This philosophy aligns with broader movements like responsible AI, value-sensitive design, and AI for social good, all of which advocate for ethical, human-guided use of technology to foster a more just and inclusive educational environment.
- Humans in the loop: Teachers interpret patterns in student data and make meaningful instructional decisions, rather than relying solely on automated systems.
- Teacher-led assessments: Formative assessments should include teacher judgment, ensuring that AI tools support—not replace—professional expertise.
- Contextual decision-making: AI lacks the nuanced understanding of context that humans possess. Teachers must remain responsible for decisions that affect student learning and well-being.
- Equity and responsibility: Educators play a critical role in ensuring AI contributes to a just and equitable educational environment, especially when decisions have long-term consequences for students.
This approach aligns with broader movements like responsible AI, AI for social good, and value-sensitive design, all of which prioritize human values, ethics, and oversight.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND THE FUTURE OF TEACHING AND LEARNING:
100 Ways to Encourage Human Input Over Artificially Generated Intelligence in Your Classroom Assignment
Academic Integrity
A word about plagiarism detectors: Some instructors may look to technological tools to address cheating concerns. Turnitin and other plagiarism detectors can provide useful instructional information to both instructors and students, but Software that claims to detect the use of AI-generated text is prone to false positives and false negatives. Research has suggested these tools are not reliable and may be biased against non-native English writers. More importantly, plagiarism detection and proctoring are based on a model of enforcement and punitive consequences that only address certain factors related to academic integrity.
Other ways to address these concerns:
- Discuss ethical implications specific to your discipline and to teaching and learning.
- Consider accessibility of generative AI tools and discuss potential biases.
- Prepare to identify and mitigate biased, discriminatory, or inaccurate AI outputs with students.
- Understand who can use or own the data AI tools receive or produce. Emphasize the importance of obtaining consent before inputting student-generated content into AI.
- Discuss copyright concerns related to AI-generated content.
Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Teaching and Learning
Evaluate Your Assignments and Assessments
Are your assignments easily completed using AI? Consider pedagogical best practices of course design as a tool to make your assignments ChatGPT resistant:
- Test out your assignments to see what generative AI does well and does poorly in your context.
- Value process over product: build in smaller scaffolding assignments; incorporate checkpoints, peer conferences, in-class discussions, multiple drafts, and reflection activities. Consider inclusion of more informal writing.
- Prioritize humanity in your course design by focusing on personal reflections, local and community perspectives, and timely and niche references. Require human interactions and the inclusion of cultural diversity.
- Emphasize creative thinking, new insights, complex analysis, and source citation.
- Assign multimedia assessments (video essays, podcasts, oral exams, presentations, etc.).
10 Best Practices for AI Assignments in HigherEd
University of Sydney Responding to Generative AI for Assessments
Develop a Syllabus Statements for AI
Instructors should carefully consider how (if at all) they will permit the use of Generative AI tools in their courses. You may begin with a Decision Tree to help you to decide your parameters. Instructors should communicate any expectations or requirements clearly with students to avoid confusion. This Artificial Intelligence Assessment Scale (Furze, 2022) is a tool that help instructors to articulate their expectations on AI use in their courses and within their respective disciplines:
The AI Assessment Scale
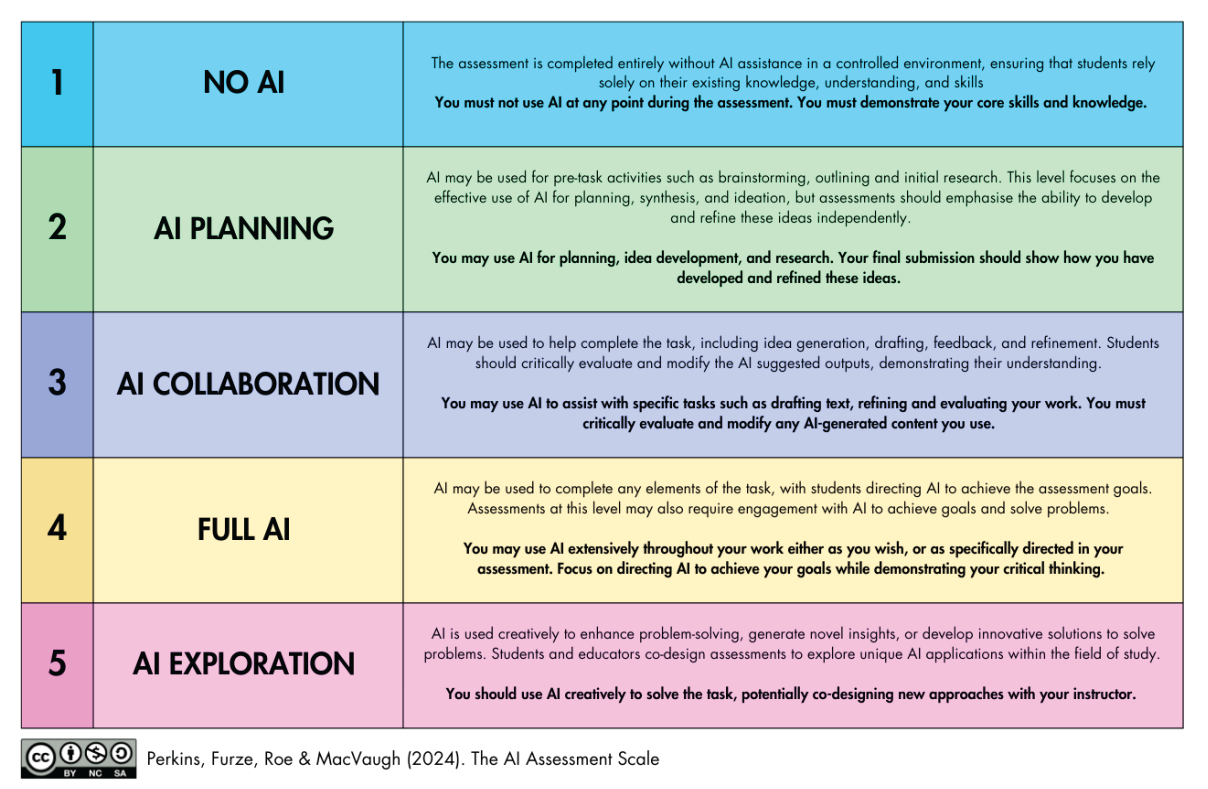
AI Assessment Scale image source
Peer Reviewed article on AI Assessment Scale
More examples:
- University of Delaware Considerations for AI tools
- Syllabi Policies for AI Generative Tools - Google Docs- Examples from several institutions
Talk to Your Students
Students will need clarity and transparency from their instructor on how to navigate this tool in your classroom and in the real world. Consider these topics to address with your students:
- Technology: Discuss with students the technology itself, including GAI's strengths, limitations, and biases. Consider scheduling a class demonstration so that students can see and experience examples of each.
- Transparency: Explain course expectations and requirements around GAI, ideally as they relate to the course's learning outcomes.
- Usage: Offer clear examples of when and how GAI can, cannot, or must not be used. If GAI is banned, explain the reasons, ideally, as they relate to the course's learning outcomes.
- Citation:If GAI is allowed and/or required, explain how to cite the use of these tools in the course. Citation and Attribution with AI Tools Instructions
- Consequences: Discuss the consequences of unauthorized use of GAI tools or a failure to acknowledge
permitted use.
For Classroom Discussion:
- Assess student familiarity with generative AI tools through an anonymous poll.
- Initiate a conversation to clarify how these tools work and GAI's benefits and pitfalls.
- Engage students in thinking about how assignments contribute to course goals, using Bloom's Taxonomy for guidance.
- Highlight relevance and value of what they are learning, emphasizing its relevance to their professions, personal growth, future academic work, or communities.
- Discuss AI and academic integrity, reflecting on the ethical implications of using generative AI.
- Prompt reflections on the purpose of writing in the learning process, including the development of their ideas and the sharing of their own unique voice.
